Understanding Laminating Resin: Applications, Types, and Benefits
What is Laminating Resin?
Definition and Basic Properties
Laminating resin is a type of synthetic polymer material primarily used in composite construction. It serves as a binding agent that incorporates and reinforces various fibers such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, or aramid fibers. Typically, laminating resins come in two main categories: polyester and epoxy resins. Each type has unique attributes that cater to specific applications, making it essential to understand their properties for optimal usage.
Basic Properties of Laminating Resins include excellent adhesion to substrates, durability, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. These properties make laminating resin a foundational element in industries ranging from marine to automotive and construction. Additionally, these resins often have a low viscosity, allowing for easy application and penetration into fabric layers.
Types of Laminating Resin
Understanding the different types of laminating resins helps you select the most suitable one for your project. The two main types are:
- Polyester Laminating Resins: These are widely used due to their affordability and ease of use. Polyester resins are known for their quick curing times and are suitable for high-volume production environments. However, they have lower mechanical properties compared to epoxy resins.
- Epoxy Laminating Resins: Epoxy resins are valued for their superior adhesion and mechanical strength. They provide better thermal and chemical resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring durable and long-lasting components. While they may be more expensive and require a more complex mixing process, their performance often justifies the investment.
Applications of Laminating Resin
Laminating resins play a crucial role in various applications, enhancing performance and longevity in different contexts:
- Marine Industry: Utilized to construct or repair boats and other maritime vessels, as the resin’s waterproof properties and strength make it ideal for aquatic environments.
- Aerospace Sector: Employed in manufacturing light yet robust components that require high-performance materials.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used for body panels, bumpers, and other components to reduce vehicle weight while maintaining structural integrity.
- Building and Construction: Laminating resins are used to fabricate composite structures in architectural design, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional strength.
- Sports Equipment: Found in the production of durable sports gear, such as bicycles and surfboards, which require lightweight yet resilient materials.
Benefits of Using Laminating Resin
Durability and Strength
One of the primary advantages of using laminating resin lies in its impressive durability. The molecular structure of these resins provides them with the strength necessary to withstand mechanical stress, environmental exposure, and chemical interaction. When used appropriately, laminating resin can significantly extend the lifespan of composite materials, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Laminating resins are designed to resist moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. This resistance is vital in applications exposed to harsh outdoor conditions or chemical environments. For example, in marine applications, the resin protects against water infiltration, which can lead to delamination and structural failures. In addition, its UV stability helps maintain structural integrity over time, preventing degradation caused by sunlight.
Cost-Effectiveness in Projects
While the initial investment in laminating resin can be higher than other binding agents, the long-term benefits often outweigh these costs. The resilience and longevity of projects utilizing laminating resin lead to savings over time, as maintenance and replacement costs drop significantly. Furthermore, the speed and ease of application reduce labor costs, making it an economically sound choice for various industries.
How to Choose the Right Laminating Resin
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right laminating resin hinges upon a myriad of factors. Some key considerations include:
- Application Requirements: Analyze the specific demands of your project, such as strength, weight, environmental exposure, and curing time.
- Type of Reinforcement Material: The resin should be compatible with the type of fiber being used, whether it’s fiberglass, carbon fiber, or another material.
- Curing Conditions: Consider the temperature and humidity levels during curing, as some resins require specific conditions to achieve optimal performance.
- Workability: Evaluate how easy it is to mix and apply the resin. Different formulations may have varying viscosity levels affecting application methods.
Specific Use Cases
By matching the properties of the laminating resin with the project requirements, you can ensure the best possible outcome. For instance:
- If you’re constructing a lightweight aircraft, an epoxy laminating resin might be necessary for its superior strength-to-weight ratio.
- For building a cost-effective mold, a polyester laminating resin could be a suitable option due to its lower cost and quick curing time.
- In applications requiring chemical resistance, such as in the production of storage tanks or pipes, opt for specialized epoxy formulations that excel in corrosive environments.
Best Practices for Selection
To optimize your selection process, here are several best practices:
- Conduct thorough research on the properties of various laminating resins to ensure proper compatibility with your project.
- Consult with industry experts or technical data sheets available from resin manufacturers to gain insights into the appropriate selection.
- Perform small-scale tests or prototypes to assess how the chosen resin behaves under real-world conditions before committing to a larger project.
Application Techniques for Laminating Resin
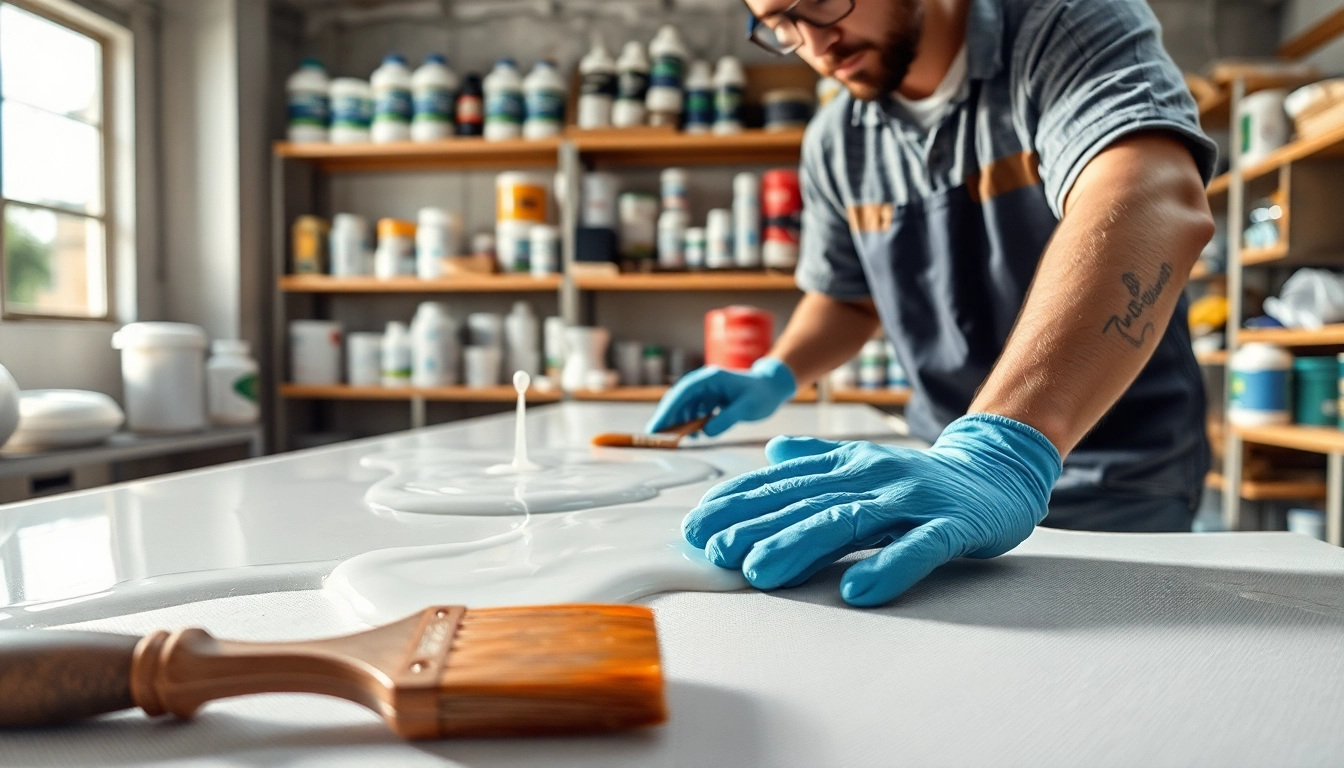
Preparing the Surface
Proper surface preparation is pivotal to the success of any laminating project. Before applying laminating resin, ensure the surface is clean, dry, and free of contaminants such as oil, grease, or moisture. Smooth surfaces may need to be sanded to create a texture that promotes better adhesion, while porous surfaces might require a primer to ensure adequate bonding.
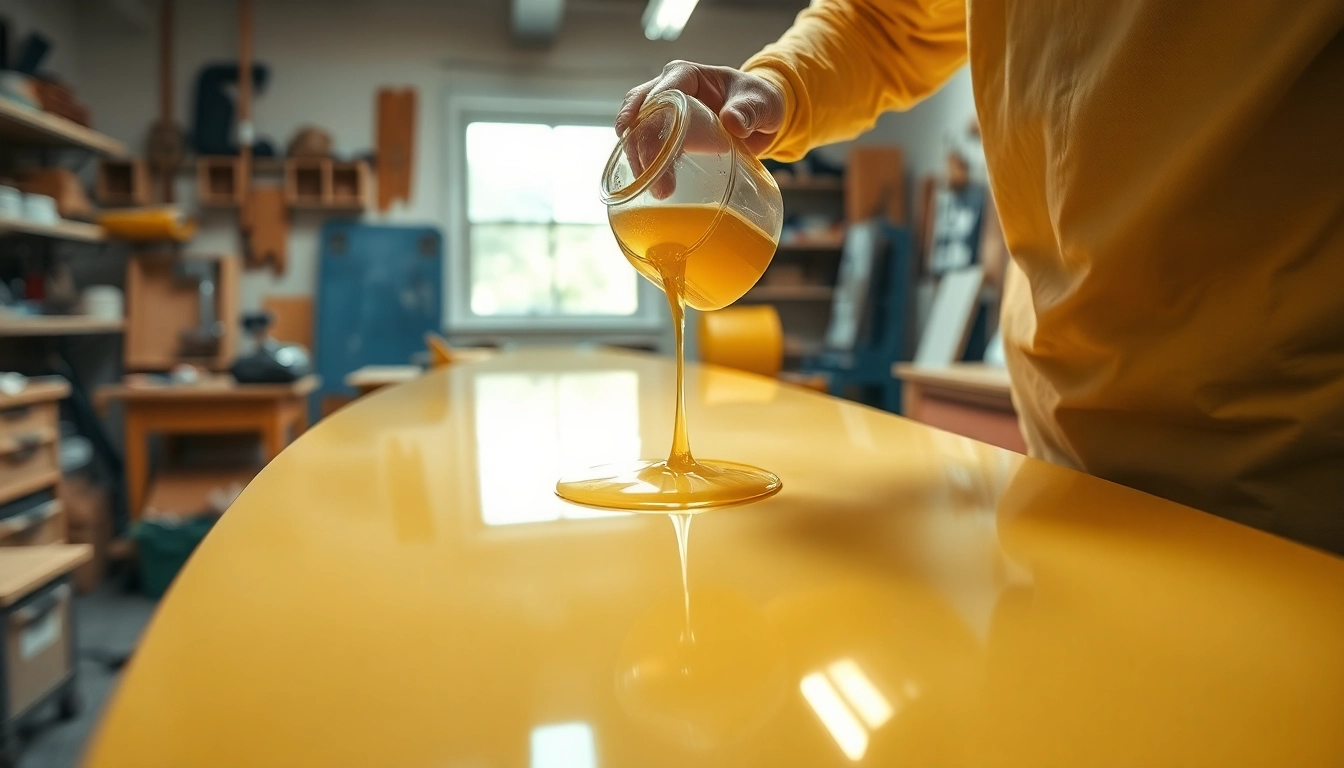
Mixing and Pouring Techniques
Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the mixing ratios for optimal performance. Proper mixing of the resin and hardener is critical to achieving the desired curing and strength properties. Pour the resin gently, ensuring it covers the entire surface to avoid creating air bubbles. Utilize tools such as brushes, rollers, or squeegees for even distribution, especially when working with larger surfaces.
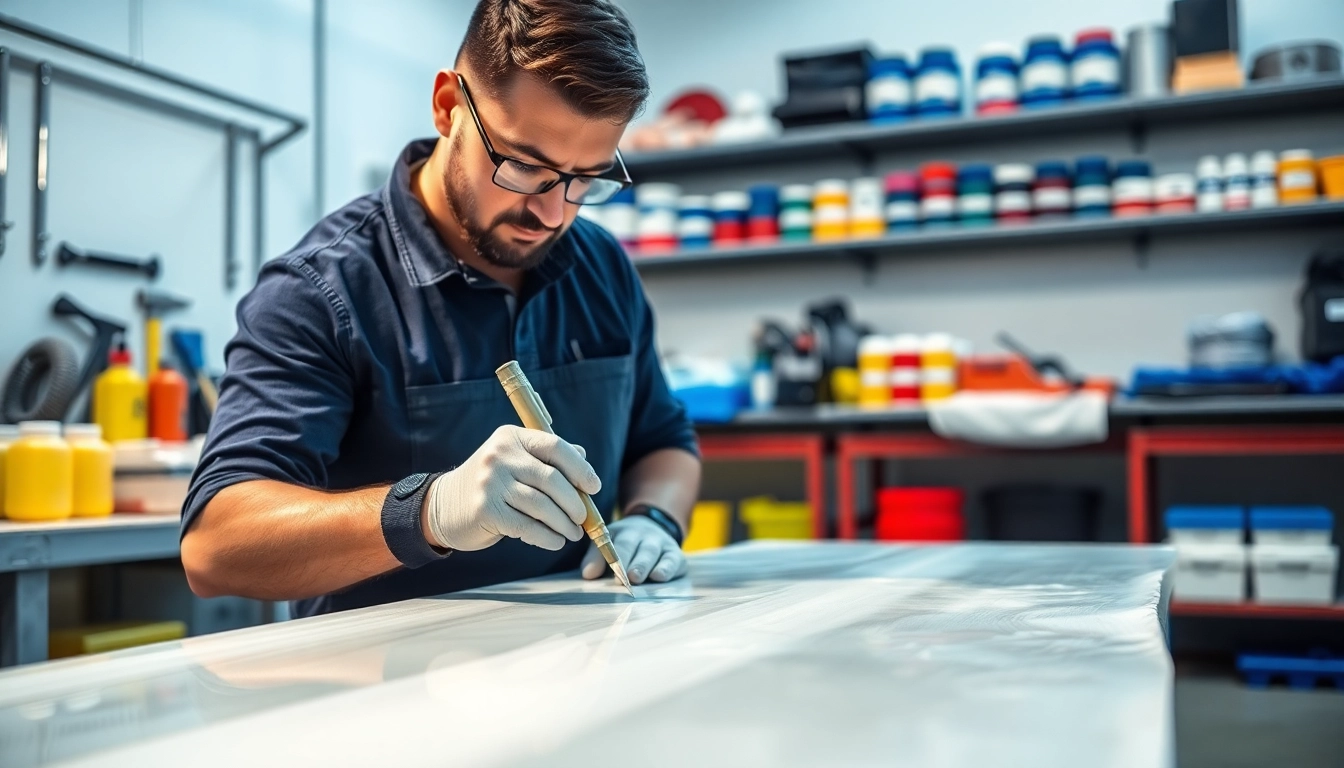
Curing and Finishing
After application, allow adequate curing time as specified by the resin manufacturer. Temperature and humidity can significantly impact curing times; warmer and drier conditions generally accelerate the process. Once cured, sanding or polishing may be necessary to achieve a smooth finish. Always avoid rushing this phase as a well-cured surface ensures the maximum strength and durability of the final product.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Laminating Resin
Poor Surface Preparation
Inadequate surface preparation can lead to a weak bond, resulting in delamination or failure of the composite. Take the time to ensure the surface is properly cleaned, textured, and primed as needed.
Incorrect Mixing Ratios
Using incorrect ratios of resin to hardener can lead to improper curing, which diminishes the resin’s strength and performance. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications for mixing components.
Ignoring Curing Time
Rushing the curing process can compromise the integrity of the laminated piece. Ensure that ample time is allowed between application and any further processing, such as sanding or painting, to ensure optimal results.












Post Comment