Mastering the Mortgage Process for Lenders: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating Home Loans
Understanding the Mortgage Process for Lenders
The mortgage process is a vital aspect of the lending landscape, particularly for lenders aiming to facilitate smooth transactions while maximizing their operational efficiency. At its core, the mortgage process for lenders involves a series of stages and interactions with various key players that ultimately lead to the approval or denial of loan applications.
Understanding these stages is crucial not only for lenders but also for brokers, financial institutions, and the borrowers themselves. One significant factor that can streamline this process is the mortgage process for lenders, which focuses on clarity, efficiency, and communication. This overview will immerse us into the intricacies of the mortgage process.
What is the Mortgage Process?
The mortgage process is the formal procedure of applying for a home loan and goes beyond just filling out forms and signing documents. It encompasses several key phases that can greatly influence the timeline, which, on average, takes between 30 to 60 days. Understanding what happens in each stage can help lenders to better prepare and manage expectations.
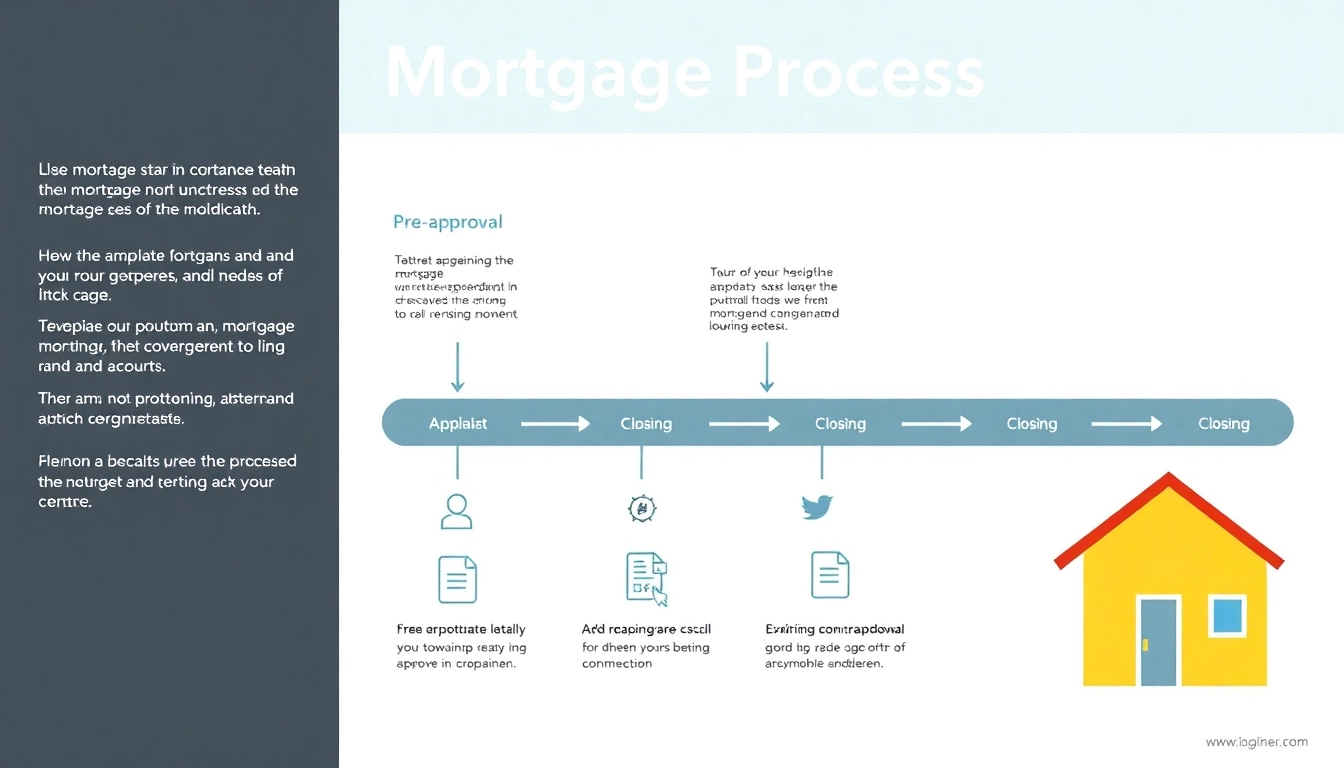
Broadly, the mortgage process can be broken down into six essential stages: pre-approval, home shopping, mortgage application, loan processing, underwriting, and closing. Each of these stages involves specific actions taken by lenders and borrowers, ensuring that all parties fulfill their obligations effectively.
Key Players in the Mortgage Process
Identifying the key players in the mortgage process is essential for lenders to understand their role in the broader context. The main players include:
- Borrowers: Individuals seeking funds to purchase a home, who must provide relevant financial and personal information.
- Lenders: Financial institutions or individuals that provide the loan, which can include banks, credit unions, and mortgage companies.
- Real Estate Agents: Professionals who assist borrowers in locating suitable properties and facilitate negotiations.
- Appraisers: Experts who evaluate the property’s worth to ensure it aligns with the amount being financed.
- Underwriters: Individuals responsible for assessing risk and determining whether the mortgage fits within the lender’s guidelines.
Each player has distinct responsibilities, influencing the mortgage process’s outcomes and timelines. Recognizing these roles allows for more efficient communication and operational execution—critical components for success.
Importance of Pre-Approval in Lending
Pre-approval is a pivotal step in the mortgage process that provides borrowers with an idea of how much they can afford to spend on a home. For lenders, pre-approval serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it demonstrates the lender’s confidence in the borrower’s capability to repay the mortgage, establishing a stronger case during negotiations. Secondly, it can expedite the process significantly, as borrowers who have been pre-approved present less risk.
Obtaining pre-approval usually requires borrowers to submit financial documentation and undergo a brief assessment of their creditworthiness. Once pre-approved, borrowers gain a competitive edge in the housing market, presenting their offers with verified purchasing power.
Five Essential Steps in the Mortgage Process
Step 1: Pre-Approval Procedures
The pre-approval process entails several important steps. Initially, borrowers will provide personal information regarding their income, debts, and assets. Lenders will conduct a preliminary credit check to ascertain the financial stability of the borrower. Key activities in this stage include:
- Gathering essential financial documents such as pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Reviewing different types of loan options available based on the borrower’s financial situation.
- Issuing a pre-approval letter outlining the terms and the maximum loan amount available to the borrower.
By completing these steps, lenders can facilitate a streamlined transition into the next phases of the mortgage process.
Step 2: The Mortgage Application
Once pre-approved, borrowers move forward to the application stage, where they formally request a specific loan. This involves filling out a mortgage application form that summarizes their financial profile, employment history, and the specifics of the property being purchased. It also entails:
- Setting a timeline for the application process and identifying necessary documentation required by the lender.
- Your lender will check the borrower’s credit profile in-depth.
- Collecting funds for application fees and beginning the deposit process.
The thoroughness and precision of the information provided during this phase significantly impact processing time and lender assessment outcomes.
Step 3: Document Collection and Submission
At this stage, lenders begin collecting necessary documents to evaluate the application further. These documents typically include comprehensive details about the borrower’s financial history, property information, and appraisals. Lenders should pay close attention to:
- Creating a clear checklist for borrowers, outlining all necessary documents.
- Maintaining communication with client and ensuring submission timelines are met.
- Employing efficient document management systems to store and process paperwork.
Effective document collection and organization can significantly mitigate delays in the approval process.
Key Challenges During the Mortgage Process
Common Roadblocks for Lenders
Despite best efforts, lenders often encounter various challenges during the mortgage process. Common roadblocks include:
- Complex Borrower Profiles: Situations involving self-employed individuals or those with varied income sources can complicate documentation and verification.
- Appraisal Delays: A slow appraisal process can cause significant setbacks, especially if the property value does not meet expectations.
- Moving Market Conditions: Fluctuating interest rates and real estate market conditions can lead to increased uncertainty for both lenders and borrowers.
Identifying these roadblocks in advance permits lenders to devise solutions, such as offering educational resources or alternative options for their clients.
Mitigating Risks in Loan Application
Risk management is crucial in the mortgage process. Risks can arise from borrower defaults, changes in market conditions, or regulatory compliance issues. Lenders can adopt several strategies to mitigate these risks:
- Implementing thorough pre-qualification checks to weed out high-risk borrowers.
- Diligently monitoring service-level agreements and compliance to prevent legal challenges.
- Utilizing data analytics and technology to predict market trends and borrower behaviors.
Incorporating these strategies can enable lenders to minimize exposure to risk while ensuring profitability and operational efficiency.
Maintaining Communication with Borrowers
Clear and consistent communication with borrowers is foundational to a smooth mortgage process. Lenders should prioritize setting expectations and ensuring that borrowers are informed throughout each phase. Best practices include:
- Providing timely updates regarding application status and any changes in requirements.
- Establishing a user-friendly platform or communication channel for borrowers to ask questions or express concerns.
- Conducting post-application follow-ups to gauge any further assistance needed by the borrower.
Responsive communication can significantly enhance borrower satisfaction and trust, which ultimately translates to higher retention rates.
Best Practices for a Smooth Mortgage Process
Streamlining Approval Workflows
Efficient workflows can drastically reduce the time it takes to process mortgage applications. Lenders can streamline their approval processes by:
- Automating routine tasks such as initial application reviews, documentation collection, and setting follow-up reminders.
- Utilizing standardized forms to ensure uniformity and completeness in submitted materials.
- Regularly assessing workflow performance to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
By adopting these measures, lenders can enhance their overall efficiency, benefiting both their operations and customer experience.
Utilizing Technology in Mortgage Processing
Technology plays a pivotal role in modernizing the mortgage process. Lenders should leverage digital solutions to facilitate better service and operational efficiency. Notable technologies include:
- Mortgage CRM Systems: These platforms aid in managing client relationships and streamlining communication.
- Online Application Portals: Allowing borrowers to submit applications and required documentation digitally enhances convenience.
- Automated Underwriting Systems: These systems enable quicker decision-making while maintaining accuracy and risk criteria.
Integrating technology into mortgage processing can offer significant improvements in turnaround times and service quality.
Enhancing Client Feedback Mechanisms
Closing the feedback loop is essential for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Engaging borrowers about their experiences during the mortgage process can yield valuable insights. Lenders can implement:
- Surveys post-transaction to assess satisfaction levels with various aspects of the borrowing experience.
- Regular check-in calls with clients to both gather feedback and maintain relationships.
- Incorporating feedback into future operational strategies to mitigate previous issues.
Utilizing client feedback not only strengthens customer loyalty but also fosters long-term growth for lenders.
Measuring Success: KPIs in the Mortgage Process
Defining Key Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a crucial role in evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of the mortgage process. Lenders should focus on quantifiable KPIs that reflect their operational goals, such as:
- Average processing time for mortgage applications.
- Approval rates versus denied applications.
- Customer satisfaction ratings post-transaction.
By defining and monitoring these KPIs, lenders can gain insights into areas needing improvement and track progress over time.
Analyzing Loan Processing Times
Loan processing time is a critical metric that affects borrower satisfaction and lender competitiveness. Lenders should aim to analyze these times across different stages of the mortgage process. Important questions to consider include:
- What is the average duration from application to approval?
- How does the time vary by loan type or borrower profile?
- Are there trends where processing times have improved or worsened over time?
Utilizing data analytics tools can assist lenders in visualizing processing times and establishing benchmarks for improvement.
Customer Satisfaction Metrics in Lending
Customer satisfaction is paramount for lenders to build lasting relationships with their clients. Implementing metrics to measure satisfaction can lead to actionable insights. Strategies can include:
- Utilizing Net Promoter Score (NPS) to evaluate the likelihood of clients recommending the lender to others.
- Implementing standardized feedback forms post-transaction to measure satisfaction levels.
- Conducting follow-up surveys to understand the borrower’s post-purchase sentiment and areas for future service improvement.
Monitoring customer satisfaction metrics allows lenders to refine their processes continuously and drive enhancements that address client needs directly.







Post Comment