Essential Guide to Nitrogen Regulators: Features, Applications, and Selection Tips
Understanding Nitrogen Regulators
What is a Nitrogen Regulator?
A nitrogen regulator is a specialized device used to control the pressure and flow of nitrogen gas from a cylinder. Highly prevalent in various industrial applications, such regulators ensure the safe, consistent, and efficient delivery of nitrogen gas under controlled pressures. Unlike ordinary pressure regulators, nitrogen regulators are designed to withstand the unique properties of nitrogen, which is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas utilized in many sectors, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and welding.
Essentially, nitrogen regulators act as a conduit that takes high-pressure nitrogen gas from the cylinder and reduces it to a lower, usable pressure. When selecting a nitrogen regulator, understanding its specifications and capabilities is paramount, particularly concerning the application it is intended for.
How Does a Nitrogen Regulator Work?
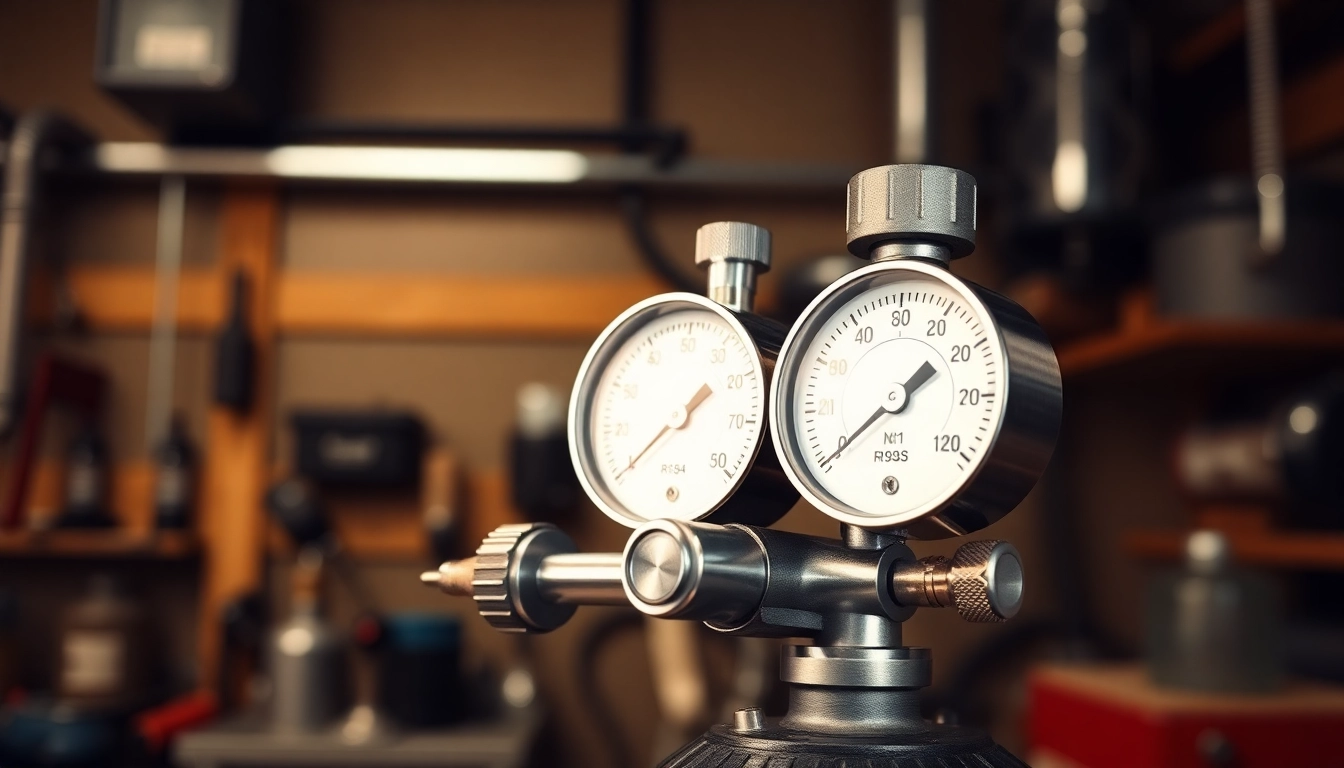
The fundamental operation of a nitrogen regulator revolves around two main components: the inlet and outlet pressures. When nitrogen gas is stored in a cylinder, it is at a high-pressure state, often exceeding 2000 PSI. The regulator receives this gas at its inlet and utilizes a diaphragm or a piston mechanism to reduce the pressure. It then allows the gas to exit at a preset and consistently regulated outlet pressure, which can typically range from 0 to 200 PSI for most applications.
This adjustment of pressure is achieved through adjustable valves that allow operators to set the desired pressure based on their specific application. Some nitrogen regulators are equipped with a pressure gauge that displays the output pressure, providing a visual cue for monitoring and adjustments.
Applications of Nitrogen Regulators
Nitrogen regulators serve as a pivotal component in various applications across numerous industries. Below are several critical applications:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Nitrogen is used for preserving food quality. Regulators are essential for maintaining optimal pressure in modified atmosphere packaging.
- HVAC and Refrigeration: Nitro-inflation agents are often utilized during system pressure testing, making nitrogen regulators integral to HVAC maintenance.
- Welding and Metal Fabrication: Nitrogen is used as a shielding gas during welding processes to prevent oxidation. Regulators ensure consistent gas flow, which is crucial for quality welds.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Nitrogen is often used to inert various systems, and regulators allow for a safe operational procedure.
Types of Nitrogen Regulators
Single-Stage vs. Dual-Stage Regulators
When selecting a nitrogen regulator, one of the first considerations is whether to go for a single-stage or a dual-stage regulator. Single-stage regulators reduce the high cylinder pressure directly to the desired outlet pressure in one step. They are often simpler in design, making them more economical and easier to use, but they can be less stable. In scenarios where fluctuations in pressure are common, a dual-stage regulator is often preferred. It ensures more stable output pressure by reducing the pressure in two steps, minimizing the variations caused by changes in the cylinder pressure.
High Pressure vs. Low Pressure Nitrogen Regulators
Nitrogen regulators can be categorized based on the pressure they manage. High-pressure regulators can handle inlet pressures exceeding 3000 PSI and are designed for industrial applications requiring robust gas delivery systems. Low-pressure regulators, on the other hand, operate in ranges under 100 PSI and cater to applications involving lighter gases and lower output signals.
Selecting between high and low-pressure regulators largely depends on the requirements of the application at hand. For instance, high-pressure regulators are essential in environments like chemical processing, where gas integrity is crucial for maintaining safety and efficacy.
Specialty Nitrogen Regulators
Some applications demand specialized nitrogen regulators, such as regulators designed for specific tasks like beverage dispensing or nitrogen purging in sensitive electronic manufacturing processes. Specialty nitrogen regulators are often tailored with unique features, including dual outlet options, upgraded sealing mechanisms, or materials specifically resistant to corrosion or chemical reaction.
Additionally, specialty models may include integrated safety features that prevent overpressure and ensure that the nitrogen flow remains consistent under varying external conditions, further enhancing safety and reliability.
Selecting the Right Nitrogen Regulator
Key Features to Consider
Choosing the right nitrogen regulator involves careful consideration of several key features:
- Pressure Ratings: Ensure the regulator accommodates the required inlet and outlet pressure specifications.
- Material Construction: Select a regulator made from robust materials like brass or stainless steel, especially for high-pressure settings.
- Regulation Mechanism: Understand whether a single or dual-stage regulator is necessary for your application demands.
- Safety Features: Look for models featuring built-in safety and overpressure relief mechanisms to enhance operational safety.
- Ease of Use: Ensure that the regulator is easy to operate for quick adjustments without extensive training.
Common Brands and Their Offerings
There are several reputable brands in the nitrogen regulator market, each with a unique offering:
- Victor: Renowned for producing durable and reliable regulators for various industrial applications.
- Smith: Offers a wide array of low and high-pressure nitrogen regulators with excellent operational control.
- Lincoln Electric: Known for its welding equipment, including precision nitrogen regulators that provide consistent performance.
- Uniweld: Specializes in gas apparatus, including nitrogen delivery systems specifically designed for HVAC and refrigeration.
Price Ranges and Budgeting Tips
The price of nitrogen regulators can vary significantly based on their specifications—generally ranging from $30 for basic models to over $300 for high-end specialty designs. When budgeting for a nitrogen regulator, consider the following tips:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine the specific requirements of your application to avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
- Compare Brands: Research and compare different manufacturers to ensure you are getting the best value for your money.
- Consider Long-term Costs: While initial costs are important, consider the lifespan and maintenance requirements that could impact total costs over time.
- Look for Warranties: Opt for products with warranties, which can provide financial protection in cases of malfunction.
Installation and Maintenance of Nitrogen Regulators
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Installing a nitrogen regulator requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols. Below is a step-by-step guide:
- Safety First: Before starting any installation, ensure you are wearing appropriate protective gear.
- Check Compatibility: Verify that the nitrogen regulator is compatible with the specific cylinder type and fittings.
- Inspect Components: Examine all parts such as hoses, fittings, and the regulator itself for signs of damage or wear.
- Attach the Regulator: Securely connect the regulator to the nitrogen cylinder, ensuring the fittings are tight to prevent leaks.
- Set Desired Pressure: Adjust the regulator to the desired outlet pressure according to your operational needs.
- Test for Leaks: Perform a leak test by applying soapy water at the connection points. Bubbles will indicate leaks, which you must rectify before using.
Regular Maintenance Practices
To ensure smooth operation and longevity of nitrogen regulators, regular maintenance is paramount:
- Periodic Inspections: Regularly inspect the regulator for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Cleaning: Clean the regulator and associated fittings regularly to avoid debris buildup that can impede function.
- Calibration: Calibration should be performed periodically to ensure accurate pressure readings and optimal performance.
- Replace Filters: If your system includes filters, replace them as recommended based on the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best nitrogen regulators may encounter problems. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- Pressure Fluctuations: If you experience fluctuating pressure, check for leaks in the fittings, or it may be necessary to recalibrate the regulator.
- Inconsistent Flow: This could be due to blockages or restrictions in the hose or fittings; ensure thorough cleaning and maintenance.
- Sealing Issues: Over time, rubber seals can degrade. Replacing these seals can resolve many pressure and leakage problems.
Safety Precautions with Nitrogen Regulators
Understanding High-Pressure Risks
Nitrogen gas operates under high pressures, creating potential hazards. Understanding these risks is crucial for safe handling:
- Explosion Risks: Improper handling of high-pressure cylinders can lead to catastrophic failure. Always ensure adequate safety measures are in place when storing and using nitrogen gas.
- Puncture Hazards: High-pressure cylinders can become hazardous projectiles if dropped or mishandled. Ensure they are secured at all times.
- Asphyxiation Hazards: In confined spaces, nitrogen can displace oxygen, leading to suffocation risks. Always ensure proper ventilation when using nitrogen in enclosed environments.
Best Practices for Safe Operation
To minimize risks when working with nitrogen regulators, follow these best practices:
- Training: Ensure that all personnel are trained in the proper handling and operation of nitrogen systems.
- Use Proper Equipment: Always utilize regulators specifically rated for nitrogen to ensure compatibility and safety.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding installation, maintenance, and operation.
- Use Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves and goggles.
What to Do in Case of Emergencies
In the event of an emergency involving nitrogen gas or regulators, follow these steps:
- Evacuate the Area: If nitrogen is leaking or causing an unsafe environment, evacuate personnel immediately.
- Alert Authorities: Notify emergency services or safety officers of the situation.
- Control the Leak: Only if it is safe to do so, attempt to turn off the nitrogen supply or secure the leak using appropriate methods.
- Provide First Aid: For anyone affected by nitrogen inhalation or asphyxiation, provide immediate first aid and call for medical assistance.








Post Comment